The Basics Of Injection Molding: A Guide To Understanding The Process
If you've ever wondered how plastic products are created, look no further than injection molding. This widely used manufacturing process is responsible for producing a wide range of products we use in our daily lives. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the basics of injection molding and provide you with a deeper understanding of the process. Whether you're a newcomer to the world of manufacturing or a seasoned professional looking to expand your knowledge, this article will provide you with valuable insights into the fascinating world of injection molding.
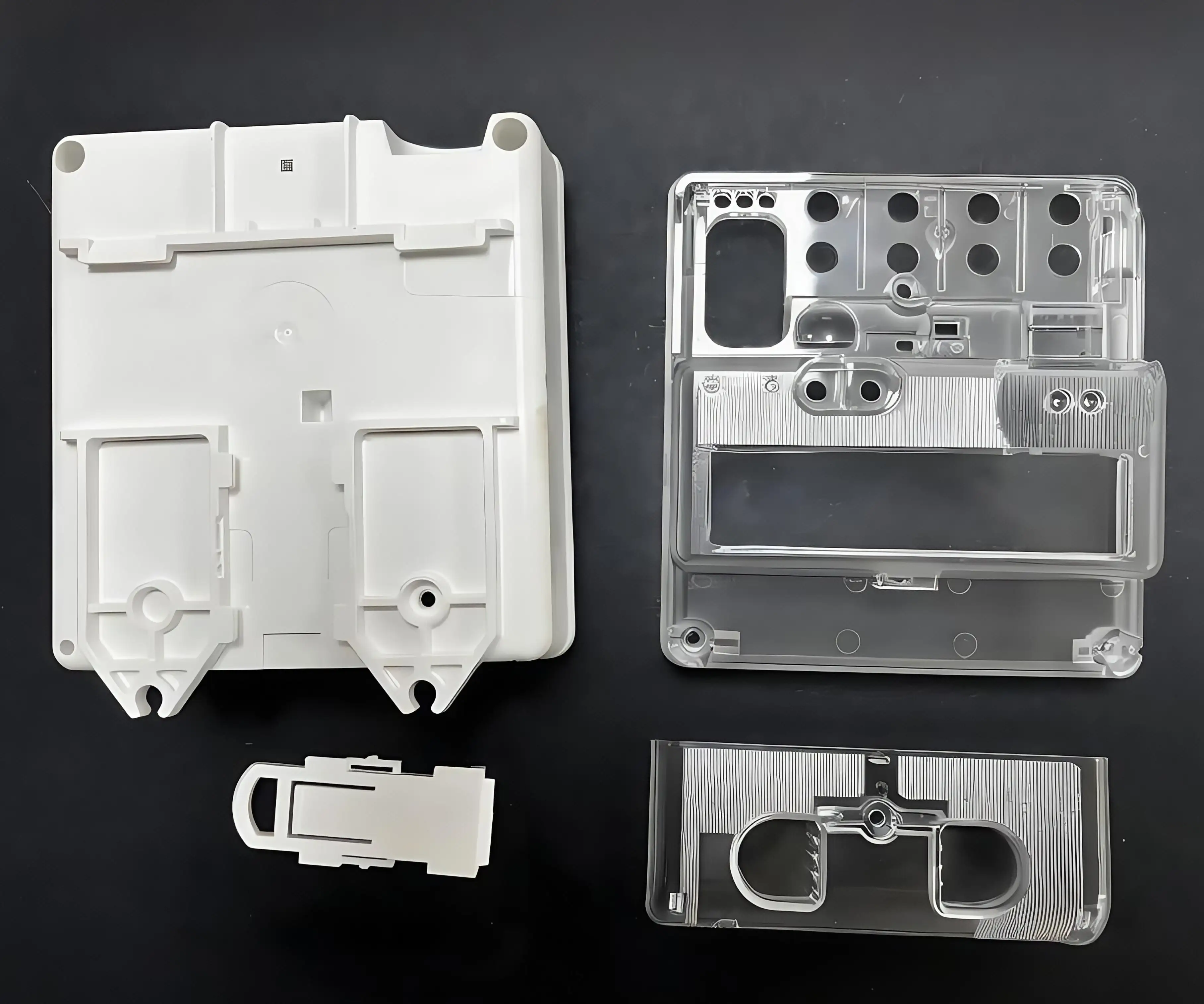

- Introduction to Injection Molding
to Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process in which molten material is injected into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into a desired shape. This process is commonly used to produce a wide range of plastic parts and products, from small components to large pieces such as automotive bumpers and medical devices. In this guide, we will provide an overview of the injection molding process, including its basic principles, key components, and common applications.
The basic principles of injection molding involve the use of a thermoplastic or thermosetting polymer material, which is heated to a molten state and then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The material is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold, resulting in a finished part that can be removed and used for various purposes. One of the key advantages of injection molding is its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision and consistency, making it a preferred choice for mass production of plastic parts.
The key components of an injection molding machine include the injection unit, the mold, and the clamping unit. The injection unit is responsible for heating and injecting the material into the mold cavity, while the clamping unit holds the mold in place and applies pressure to keep it closed during the injection and cooling processes. The mold itself is carefully designed to create the desired shape of the finished part, with the ability to produce multiple parts in a single cycle for increased efficiency.
Injection molding is commonly used in a variety of industries, including automotive, consumer goods, electronics, and medical devices. In the automotive industry, injection molding is used to produce interior and exterior components such as dashboards, bumpers, and door panels. In the consumer goods sector, it is used to manufacture items such as containers, packaging, and toys. In the medical device industry, injection molding is crucial for producing components such as syringes, tubing, and surgical instruments with high precision and quality.
Overall, injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that offers numerous benefits for producing plastic parts and products. By understanding the basic principles and components of injection molding, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and achieve high-quality results. Whether you are a novice or an experienced professional in the field of manufacturing, mastering the fundamentals of injection molding is essential for success in this competitive industry.
- How Injection Molding Works
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process in which molten material is injected into a mold, solidifies, and then is ejected as a finished product. This process is commonly used in the production of plastic parts and products, and is known for its efficiency, versatility, and high precision.
The process of injection molding begins with the raw material, usually in the form of small plastic pellets, being heated and melted in a machine known as an injection molding machine. The molten material is then injected into a mold, which is typically made of metal and has the desired shape of the finished product. The pressure and speed at which the material is injected into the mold can be controlled to achieve the desired properties of the finished product.
Once the material has been injected into the mold, it is allowed to cool and solidify, taking on the shape of the mold. This process typically takes only a few seconds, making injection molding a fast and efficient manufacturing process. After the material has solidified, the mold is opened and the finished product is ejected. The mold is then closed and the process can be repeated to create multiple identical parts.
There are many advantages to using injection molding for manufacturing plastic parts and products. One of the main advantages is the high level of precision that can be achieved with this process. Injection molding allows for intricate and complex shapes to be created with very tight tolerances, making it ideal for producing parts with exact specifications. Additionally, injection molding is a highly efficient process, with minimal waste and a high production rate. This makes it a cost-effective option for large-scale production.
Injection molding is also a versatile process, as it can be used to produce a wide range of products in various shapes and sizes. This makes it a popular choice for industries such as automotive, medical, consumer goods, and electronics. The ability to create custom molds for specific products allows for a high degree of customization and flexibility in the manufacturing process.
In conclusion, injection molding is a key manufacturing process that is widely used in the production of plastic parts and products. Its efficiency, precision, and versatility make it an ideal choice for many industries. By understanding how injection molding works, manufacturers can optimize their production processes and create high-quality products with ease.
- Key Components of the Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is a complex process that is widely used in manufacturing various products, from household items to automotive components. In order to have a comprehensive understanding of the injection molding process, it is important to learn about its key components. These components are essential for ensuring the success of the molding process and the quality of the final products.
One of the key components of the injection molding process is the mold. The mold is where the molten material, usually plastic, is injected under high pressure to form the desired shape. The mold is typically made of metal, such as steel or aluminum, and is designed to withstand the high pressures and temperatures of the injection molding process. The mold also needs to be carefully designed to ensure that the final product has the desired dimensions and surface finish.
Another important component of the injection molding process is the injection unit. The injection unit consists of the barrel, the screw, and the heater bands. The barrel is where the plastic pellets are heated and melted, while the screw is responsible for pushing the molten plastic into the mold. The heater bands help maintain the temperature of the molten plastic, ensuring that it remains in a liquid state during the molding process. The injection unit plays a crucial role in controlling the quality and consistency of the final products.
The clamping unit is another key component of the injection molding process. The clamping unit is responsible for holding the mold in place and applying the necessary pressure during the injection process. This unit consists of the clamping mechanism, the mold platens, and the hydraulic system. The clamping mechanism holds the mold in place while the hydraulic system applies the necessary pressure to ensure that the mold is securely closed during the injection process. The mold platens provide support to the mold and help distribute the pressure evenly across the mold.
The cooling system is also an essential component of the injection molding process. After the molten plastic is injected into the mold and solidifies, it needs to be cooled down quickly to maintain its shape and dimensions. The cooling system typically consists of water channels or air vents that help dissipate the heat from the mold. Proper cooling is essential for preventing warping or shrinkage of the final product, as well as ensuring consistent quality across multiple parts.
In conclusion, the injection molding process is a complex and intricate manufacturing technique that relies on several key components to ensure its success. Understanding these components, such as the mold, injection unit, clamping unit, and cooling system, is crucial for achieving high-quality and consistent results. By mastering these key components, manufacturers can optimize their injection molding processes and deliver superior products to their customers.
- Types of Materials Used in Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold to create various types of products. The process is used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods. One of the key aspects of injection molding is the types of materials used in the process.
There are several types of materials used in injection molding, each with its own unique properties and advantages. The most common materials used in injection molding are thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers.
Thermoplastics are the most commonly used materials in injection molding. These materials are able to be melted and re-melted multiple times without degrading their properties, making them ideal for recycling. Some of the most common thermoplastics used in injection molding include polyethylene, polystyrene, and polypropylene. These materials are known for their toughness, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
Thermosets are another type of material used in injection molding. Unlike thermoplastics, thermosets undergo a chemical reaction during the molding process that causes them to harden permanently. This makes thermosets ideal for applications where heat resistance and dimensional stability are important. Common thermoset materials used in injection molding include epoxy, phenolic, and polyester resins.
Elastomers, also known as rubber materials, are used in injection molding to create flexible and durable products. Elastomers have the ability to return to their original shape after being stretched or deformed, making them ideal for applications that require elasticity and resilience. Some common elastomers used in injection molding include silicone, polyurethane, and natural rubber.
In addition to these main categories of materials, there are also specialty materials that are used in injection molding for specific applications. For example, conductive polymers can be used in electronics manufacturing, while biodegradable plastics are used in environmentally-friendly products.
When selecting a material for injection molding, it is important to consider a number of factors, including the desired properties of the final product, the production volume, and the cost. It is also important to consider the molding process itself, as different materials may require different processing parameters to achieve optimal results.
In conclusion, the types of materials used in injection molding play a crucial role in the overall success of the manufacturing process. By understanding the properties and advantages of different materials, manufacturers can select the best material for their specific application and create high-quality products efficiently.
- Common Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that is widely used across various industries. This technique involves injecting molten material into a mold cavity, allowing it to cool and solidify into the desired shape. In this article, we will explore some of the common applications of injection molding and how it is used in different industries.
One of the most common applications of injection molding is in the production of plastic parts. The automotive industry, for example, relies heavily on injection molding to create components such as bumpers, dashboards, and interior trim. This process allows for the rapid and cost-effective production of high-quality parts that are durable and precise in their dimensions.
Injection molding is also widely used in the consumer goods industry, where it is employed to manufacture items such as appliance parts, packaging, and toys. The ability to mass-produce complex shapes with tight tolerances makes injection molding an ideal choice for producing a wide range of consumer products. From plastic bottles to electronic housings, injection molding is a versatile and efficient process that helps meet the demands of a competitive market.
In the medical industry, injection molding plays a crucial role in the production of devices and equipment that require precision and consistency. Components such as syringes, catheters, and surgical instruments are often made using this method, as it allows for the creation of sterile and high-quality products that are essential for patient safety. The ability to produce medical devices in large quantities while maintaining strict quality control standards makes injection molding a valuable tool in the healthcare sector.
Another important application of injection molding is in the manufacturing of aerospace and defense components. The aerospace industry requires parts that are lightweight, strong, and resistant to extreme temperatures, making injection molding an attractive option for producing components such as aircraft interiors, engine parts, and satellite components. With the ability to create complex geometries and high-performance materials, injection molding meets the stringent requirements of the aerospace and defense sectors.
In addition to these industries, injection molding is also used in the production of electronic components, household goods, and industrial equipment. The adaptability and efficiency of this manufacturing process make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications, from small-scale production runs to mass production of millions of parts.
In conclusion, injection molding is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that is essential for creating a wide variety of products across different industries. From automotive components to medical devices, this method offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, precision, and scalability. By understanding the common applications of injection molding, manufacturers can harness the full potential of this technology to meet the demands of a competitive marketplace.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the basics of injection molding is crucial for anyone involved in the manufacturing industry. By grasping the key concepts of this process, you can optimize your production efficiency, reduce costs, and create high-quality products. From selecting the right materials to designing the perfect mold, every step plays a vital role in the success of your injection molding project. With the knowledge gained from this guide, you are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of injection molding and achieve your desired outcomes. Embrace the principles of this process, experiment with different techniques, and continually strive for innovation to take your manufacturing capabilities to new heights. Remember, the possibilities with injection molding are endless – it’s time to unleash your creativity and unlock the full potential of this versatile manufacturing technique.